3D GBR for the treatment of bone atrophy on the Esthetic Zone
Dr. David González
DDS, M.Sc, PhD Master in Periodontics EFP and PhD Doctor at Complutense University of Madrid.
Private practice at Clínica Ortoperio in Murcia, Spain.
Facts
Patient:
21 years old woman, non-smoker, medically healthy.
Clinical problem:
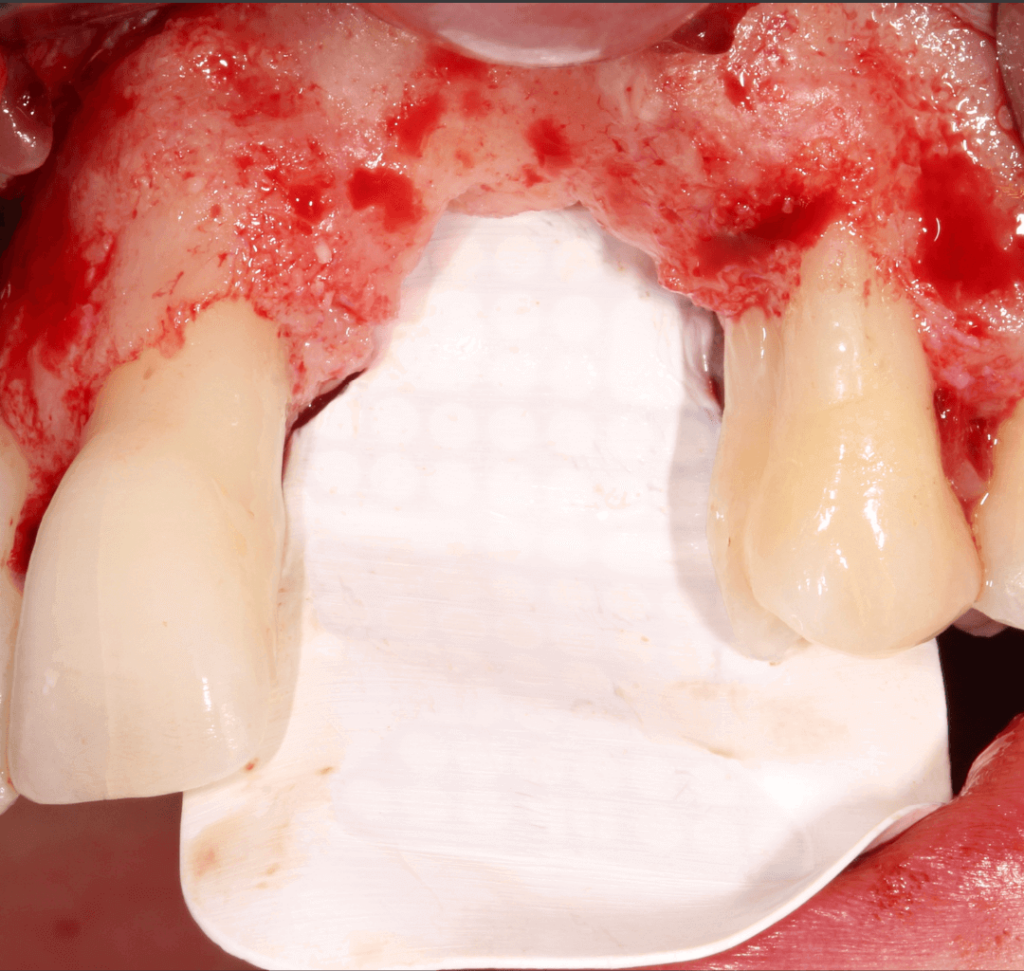
Patient presented a severe periimplantitis at 22 and 23 with no papilla and a gingival recession between them and a papilla loss at distal aspect of tooth 21. Aesthetic was severely affected since the patient gad gummy smile.
Clinical solution:
Explantation and Guided Bone Regeneration using a PTFE, Ti-reinforced NeoGen® membrane and 100% autogenous bone.
Treatment plan:
- Explantation of implants at 22 and 23.
- 3 months later: (which turned out to be 2 years later because the patients was treated and failed elsewhere): 3D guided bone regeneration using 100% autogenous bone and a PTFE, Ti-reinforced NeoGen® membrane which was fixed by Neoss Tacks.
- 1 year later: Reentry and implant placement at 23 + connective tissue graft to solve the papilla loss at distal aspect of tooth 21.
- 2 months later: Free connective tissue to reposition the mucogingival line.
- 2 months later: 2nd surgical phase and temporary restoration.
- 2 years later: Final prosthesis.
- 4 years later: Clinical and Radiographic Evolution of the Aesthetic Zone.
Products:
1 NeoGen Ti-Reinforced PTFE Membrane.
Conclusion:
3D guided bone regeneration using an e-PTFE, Ti-reinforced NeoGen® membrane and 100% autogenous bone is a fully predictable treatment for the severe hard and soft tissue atrophy on the Aesthetic Zone. This statement is supported not only by panoramic and periapical x-rays, but also by CBCT sectional cuts where we can see the complete stability of the regenerated bone.
Step by step
Step by step
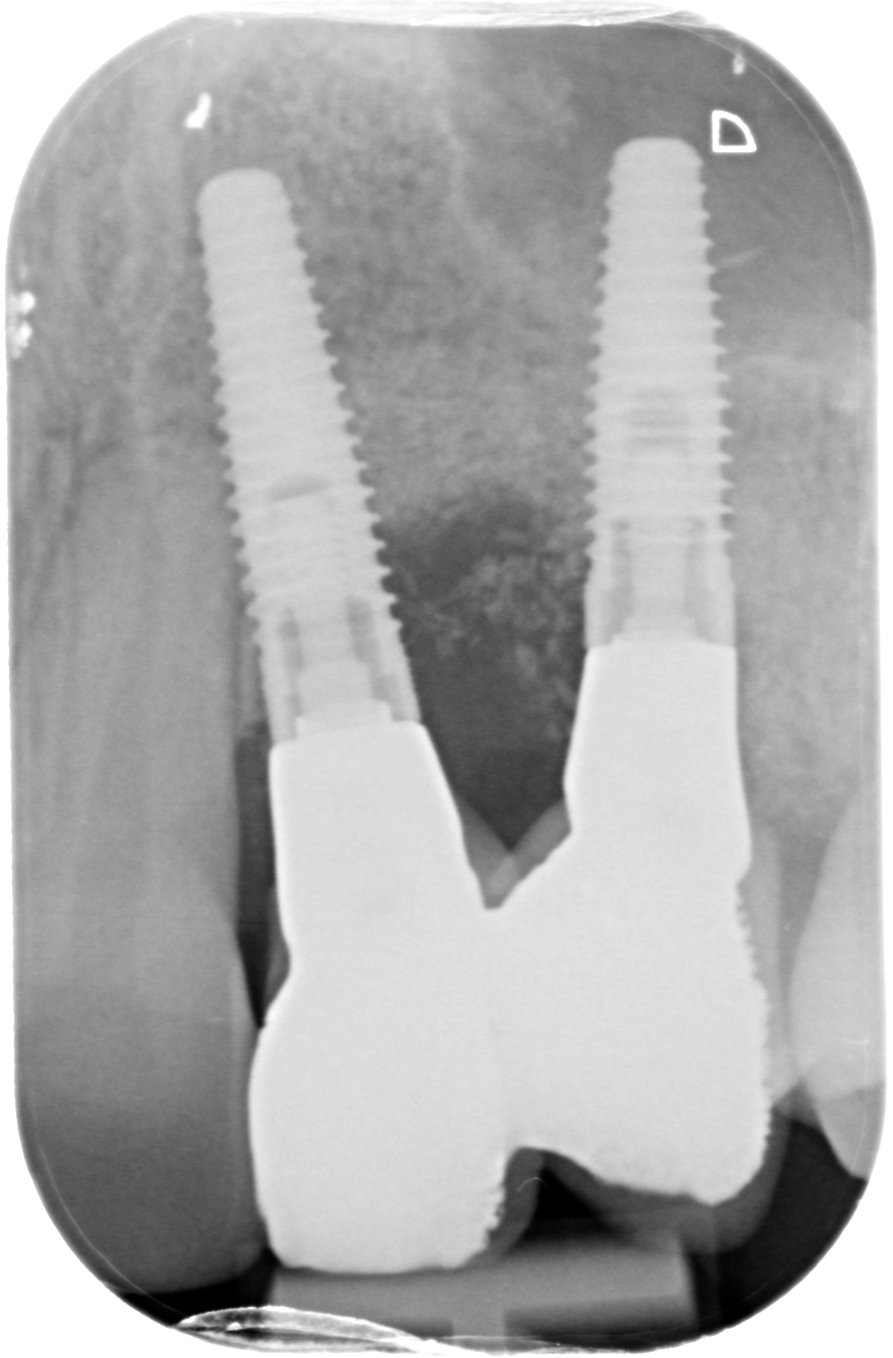
Figure 1.
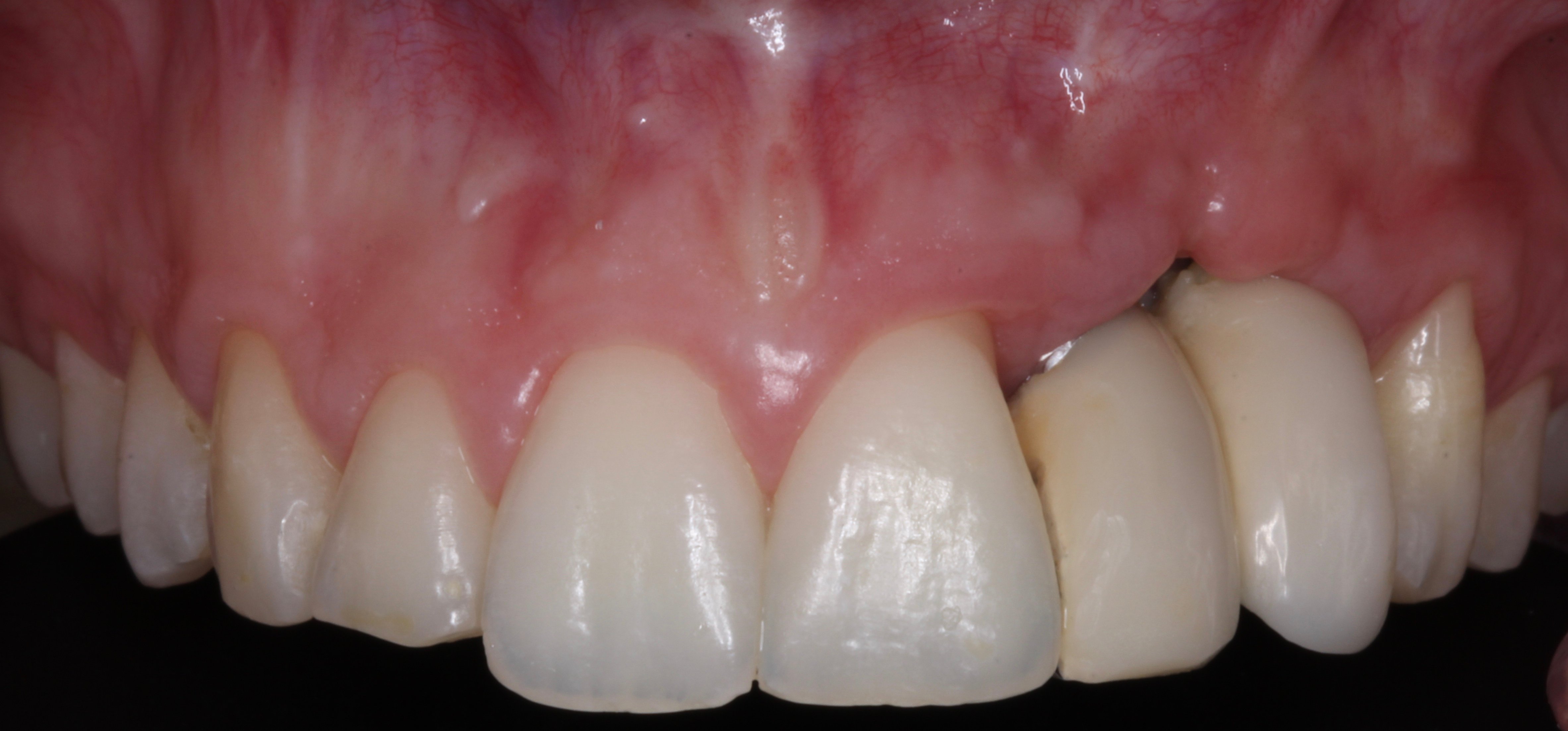
Figure 2.
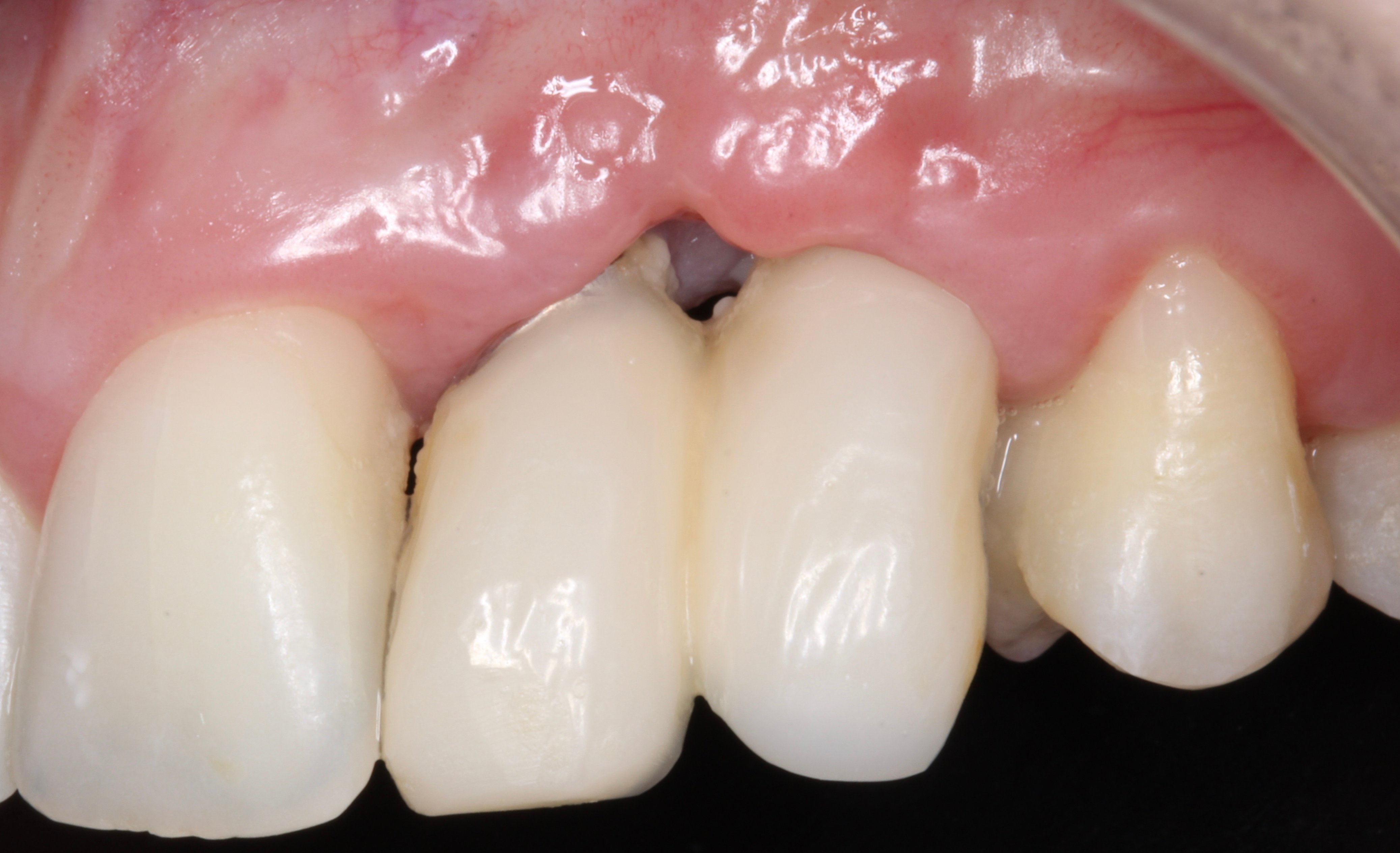
Figure 3.
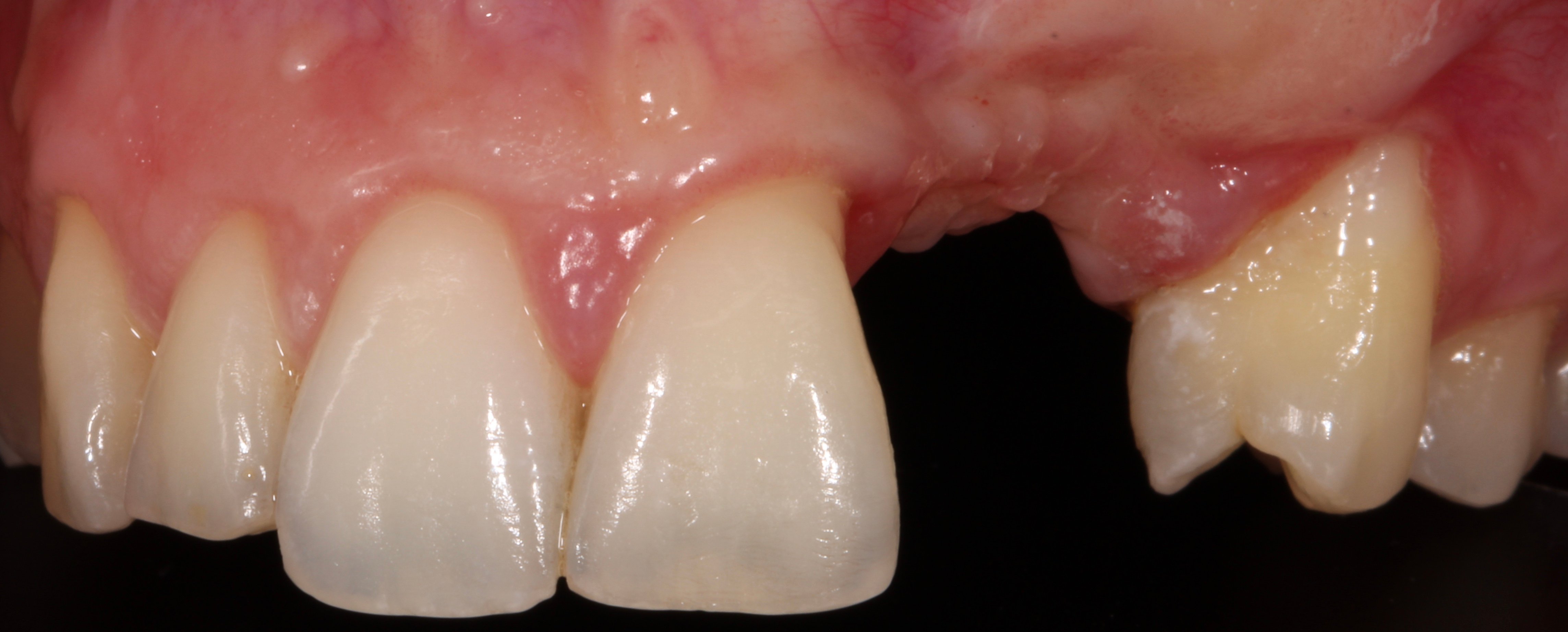
Figure 4.
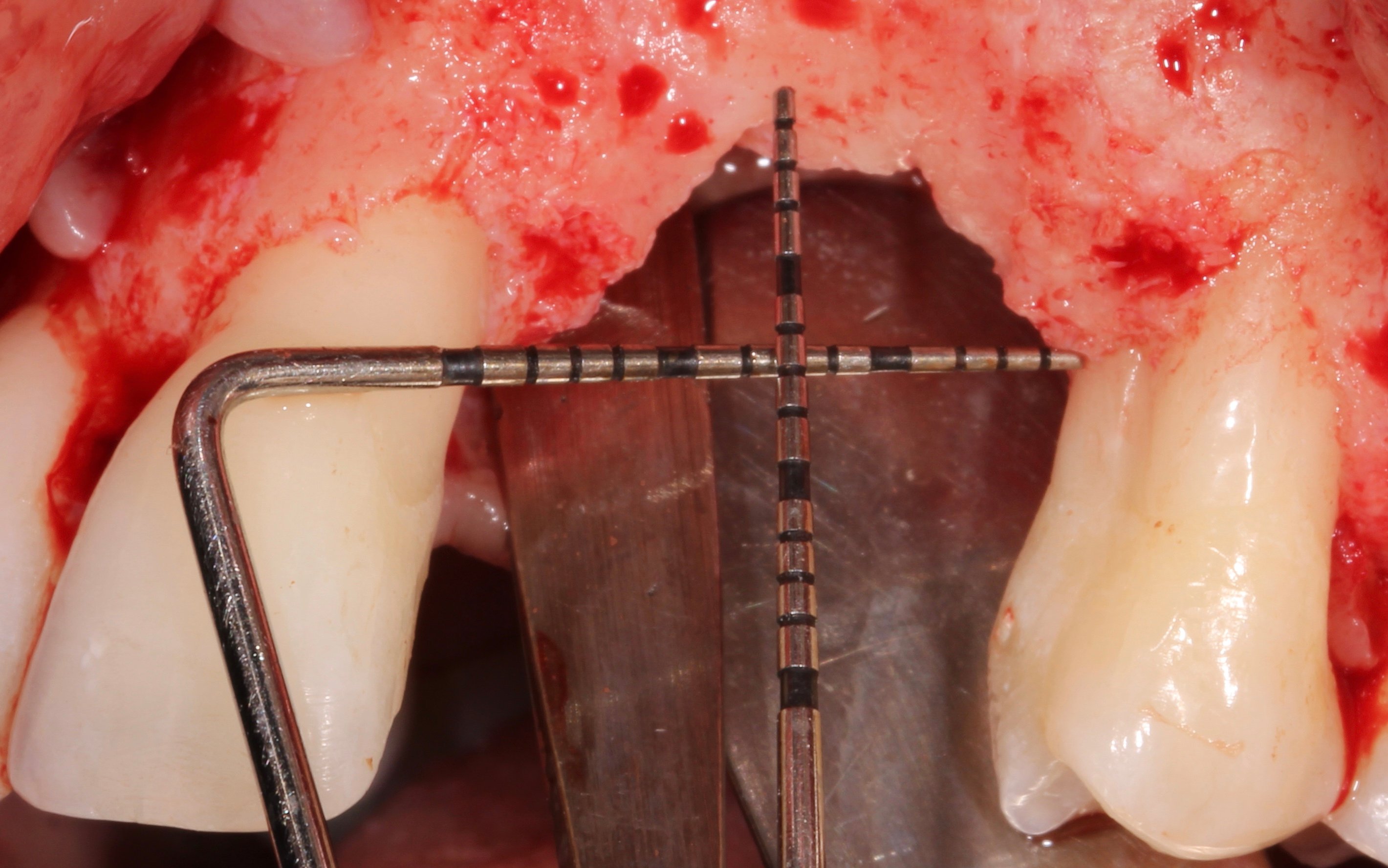
Figure 5.
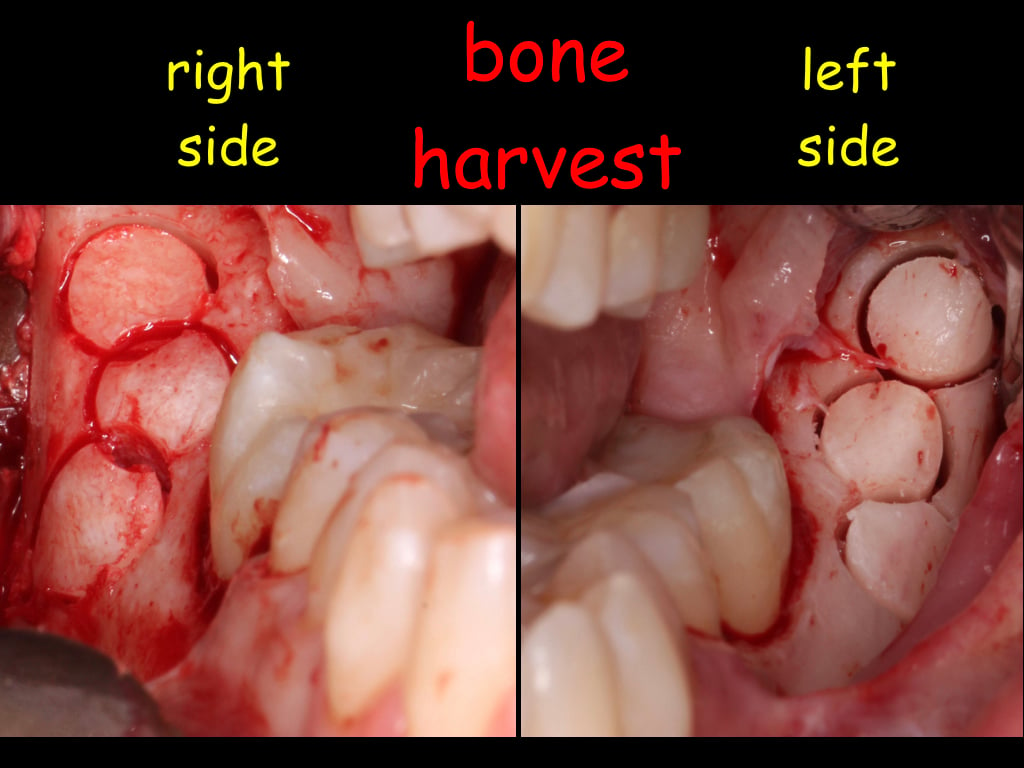
Figure 6.
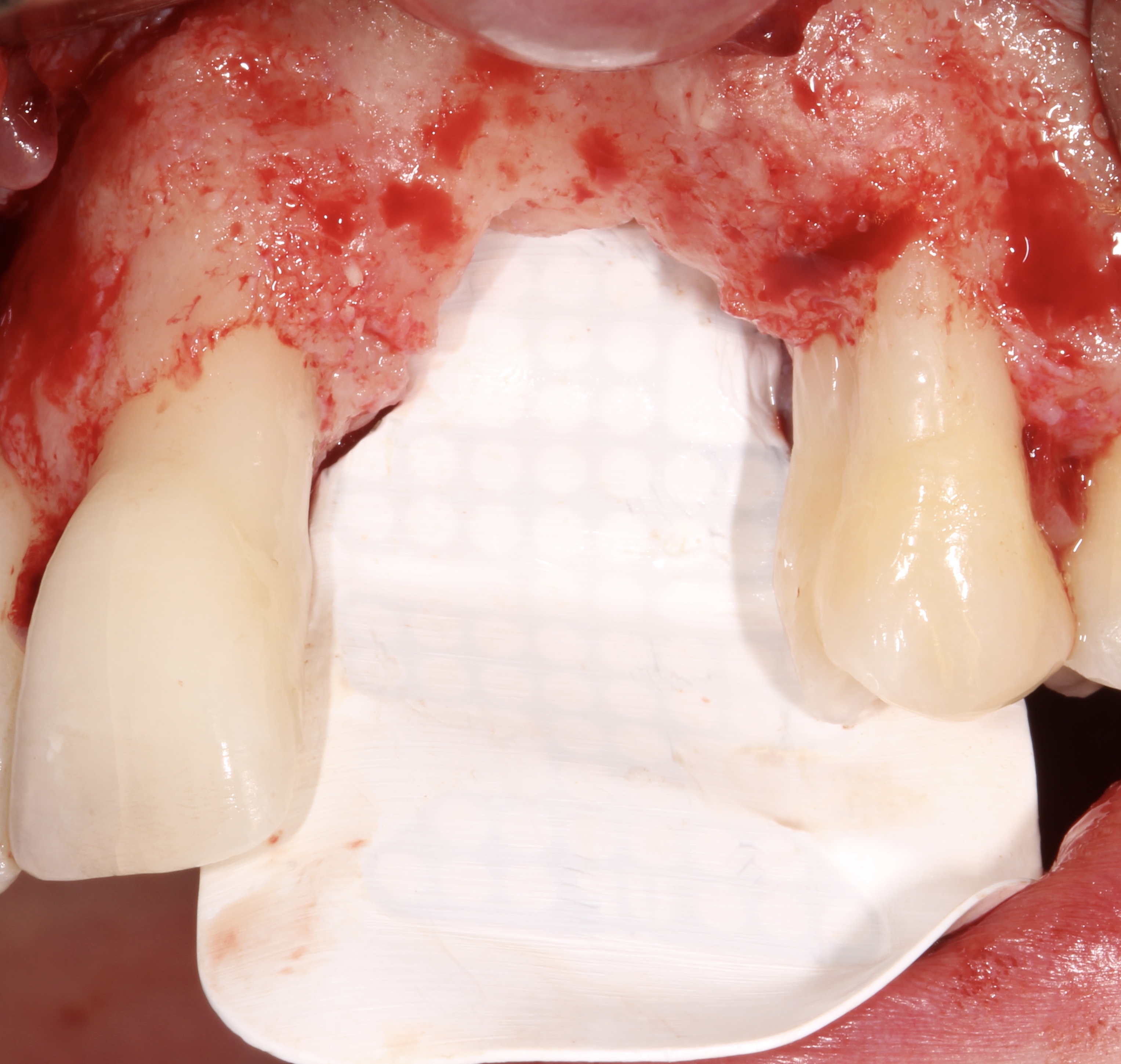
Figure 7.
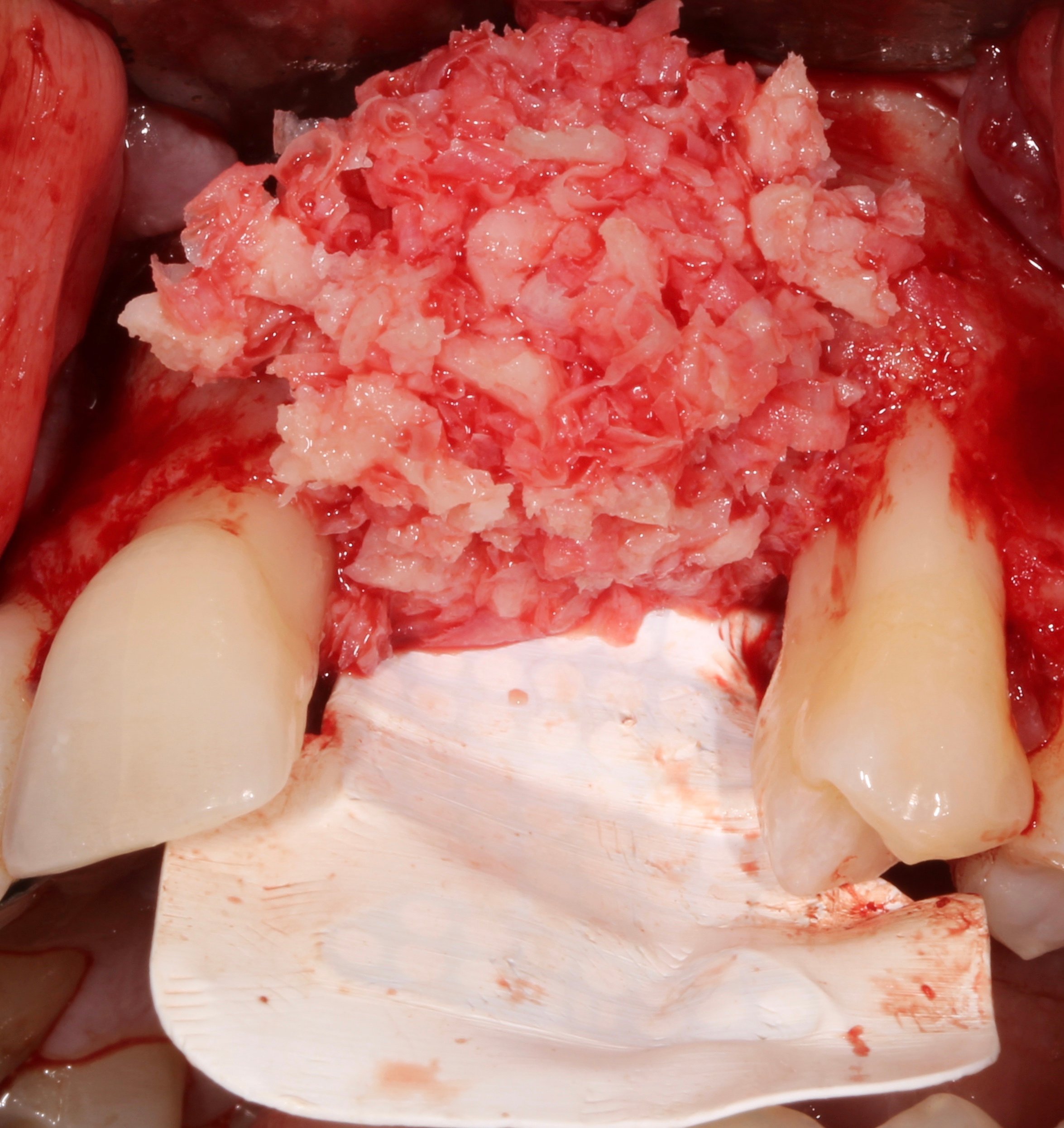
Figure 8.
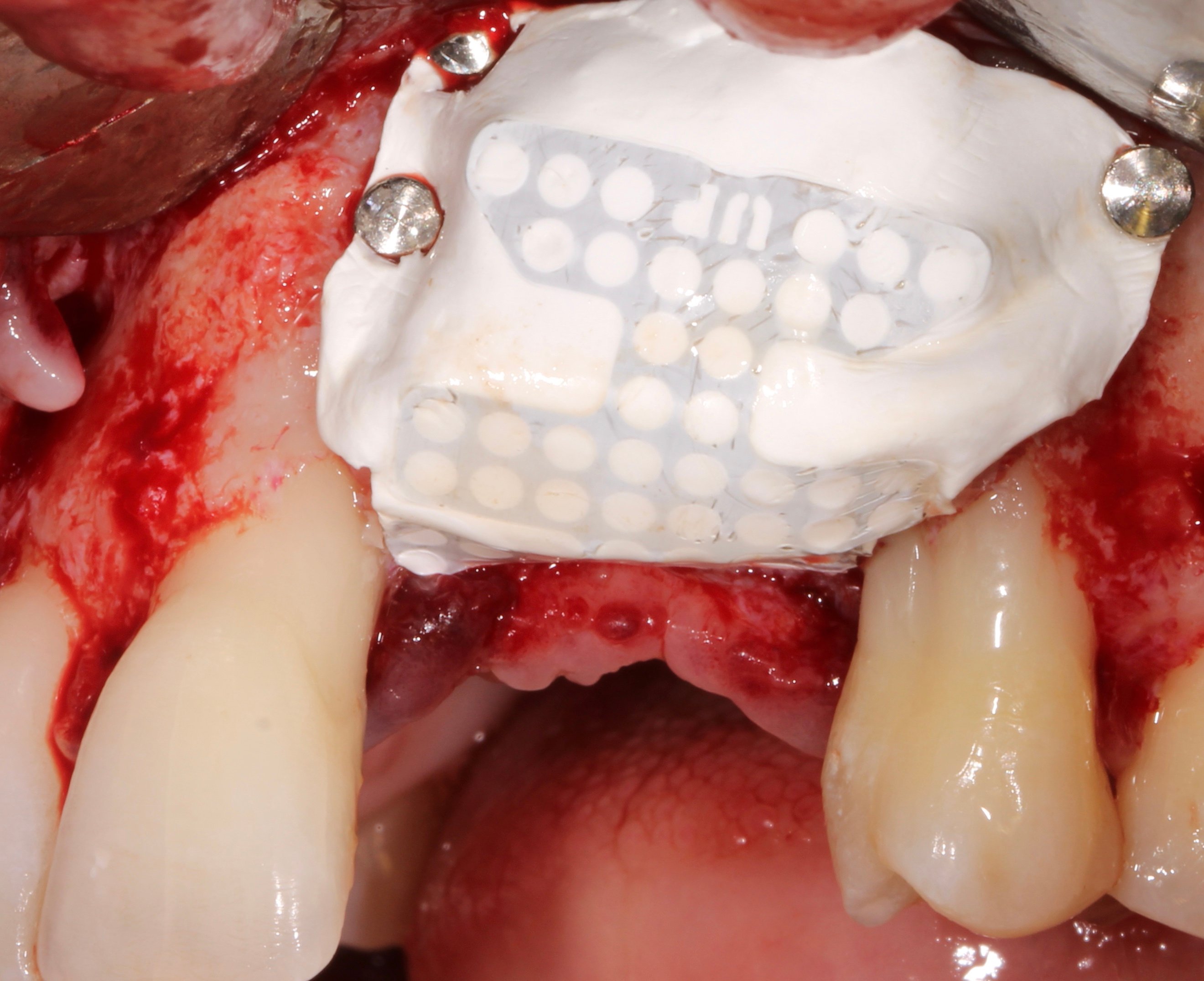
Figure 9.
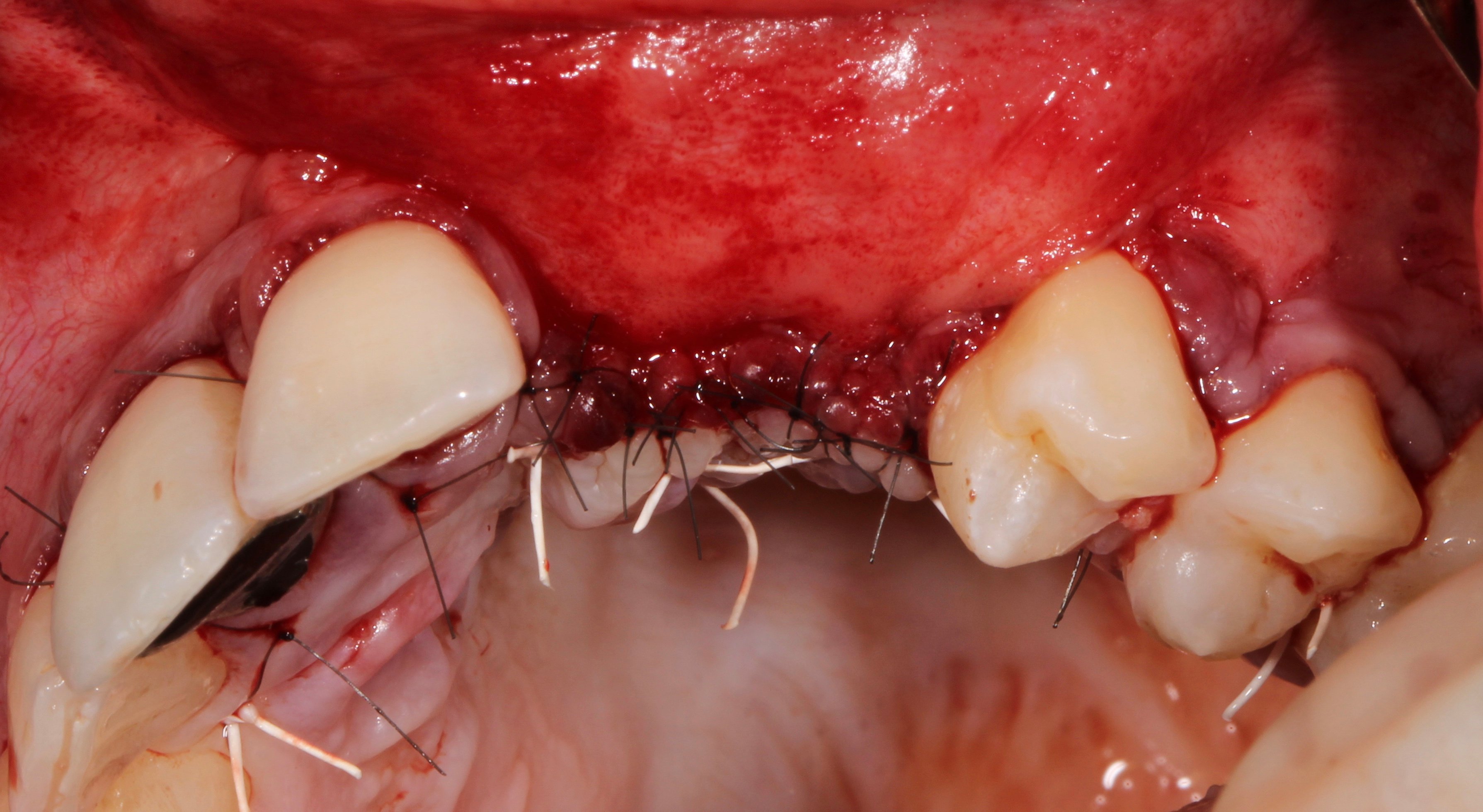
Figure 10.
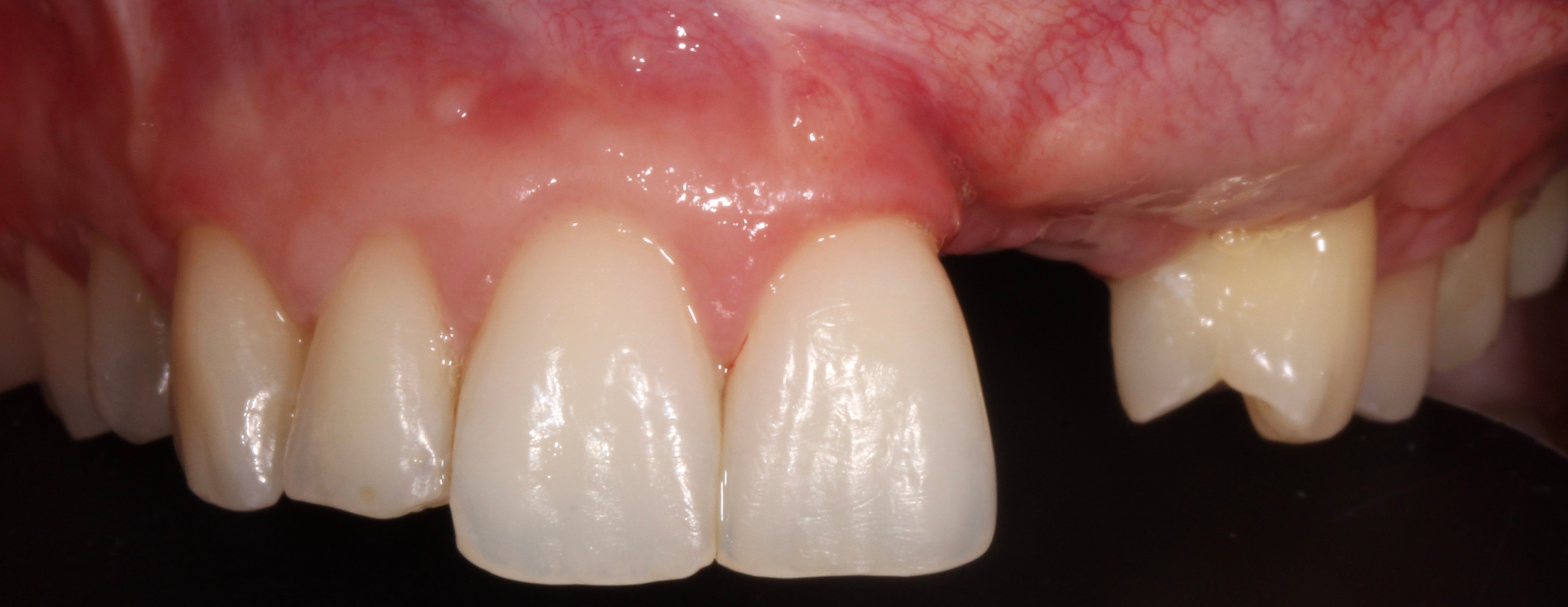
Figure 11.
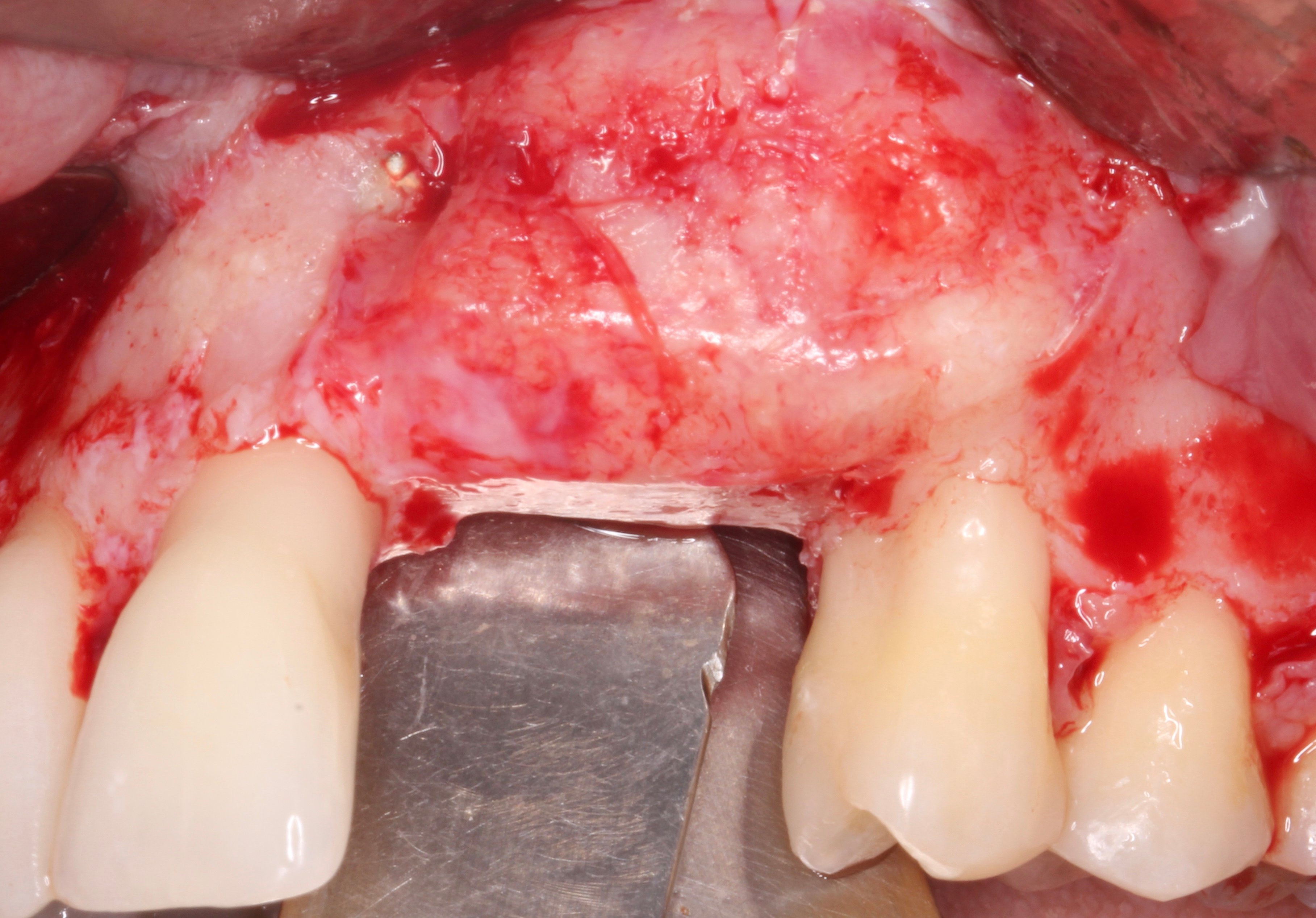
Figure 12.
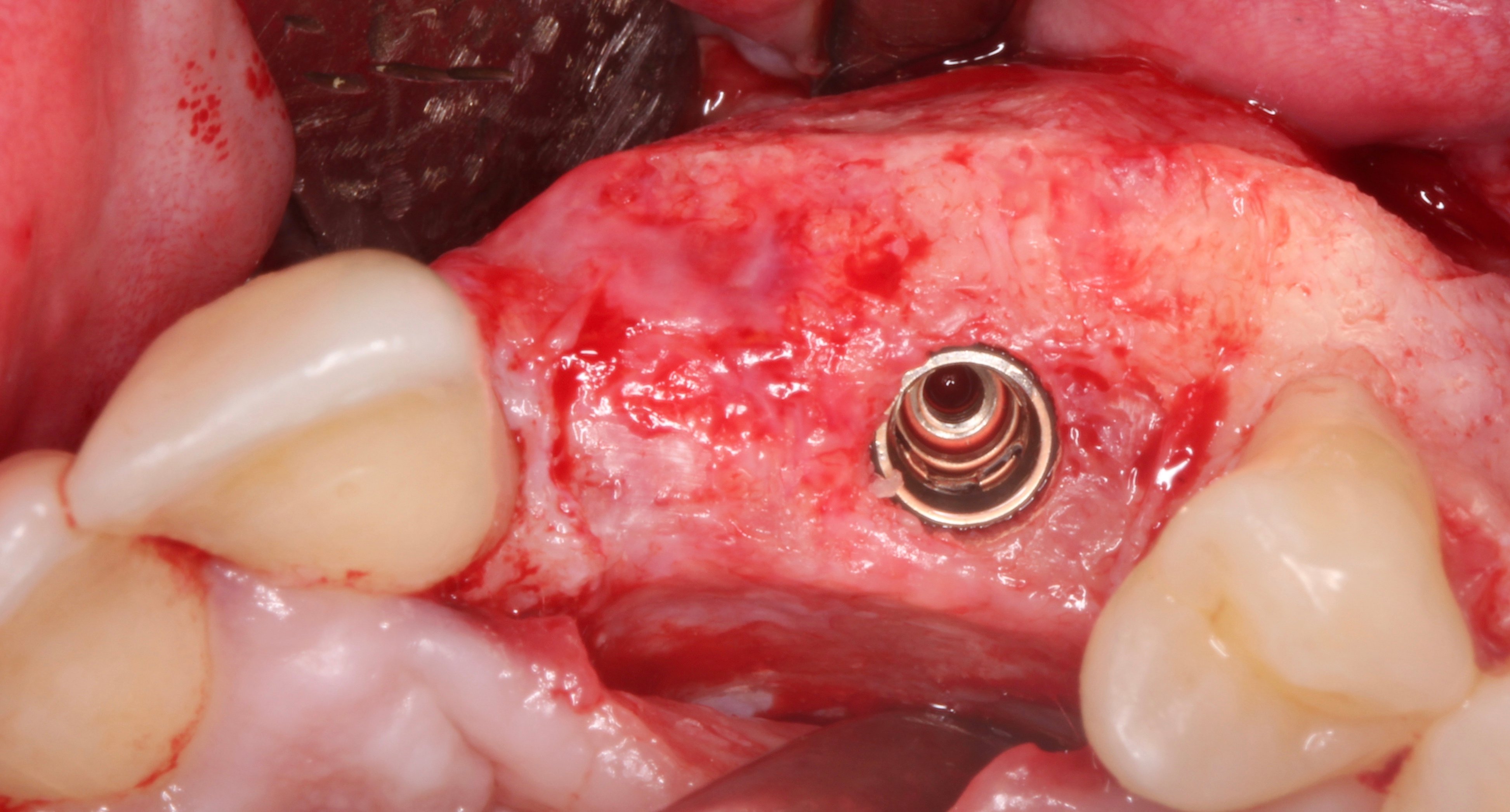
Figure 13.
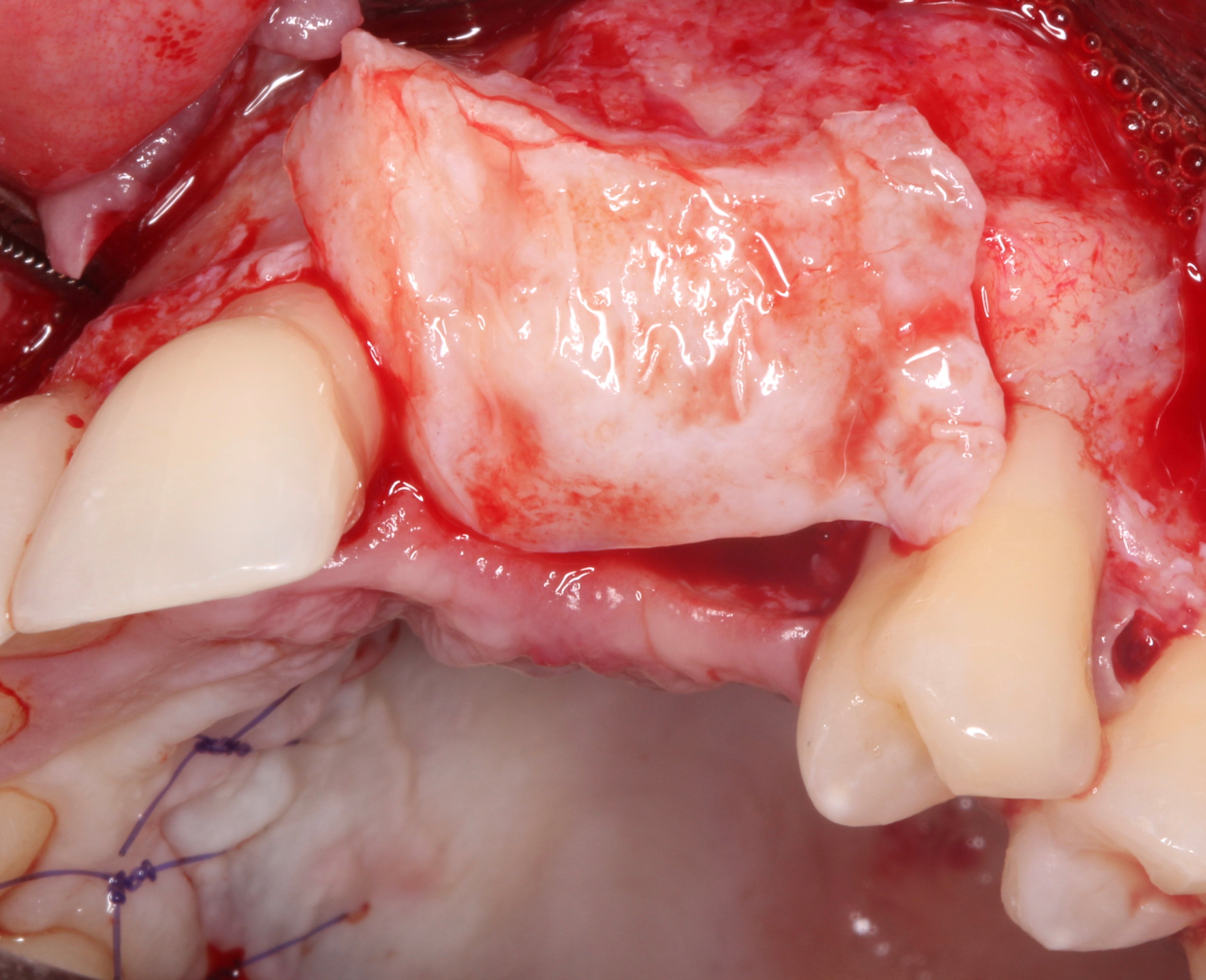
Figure 14.
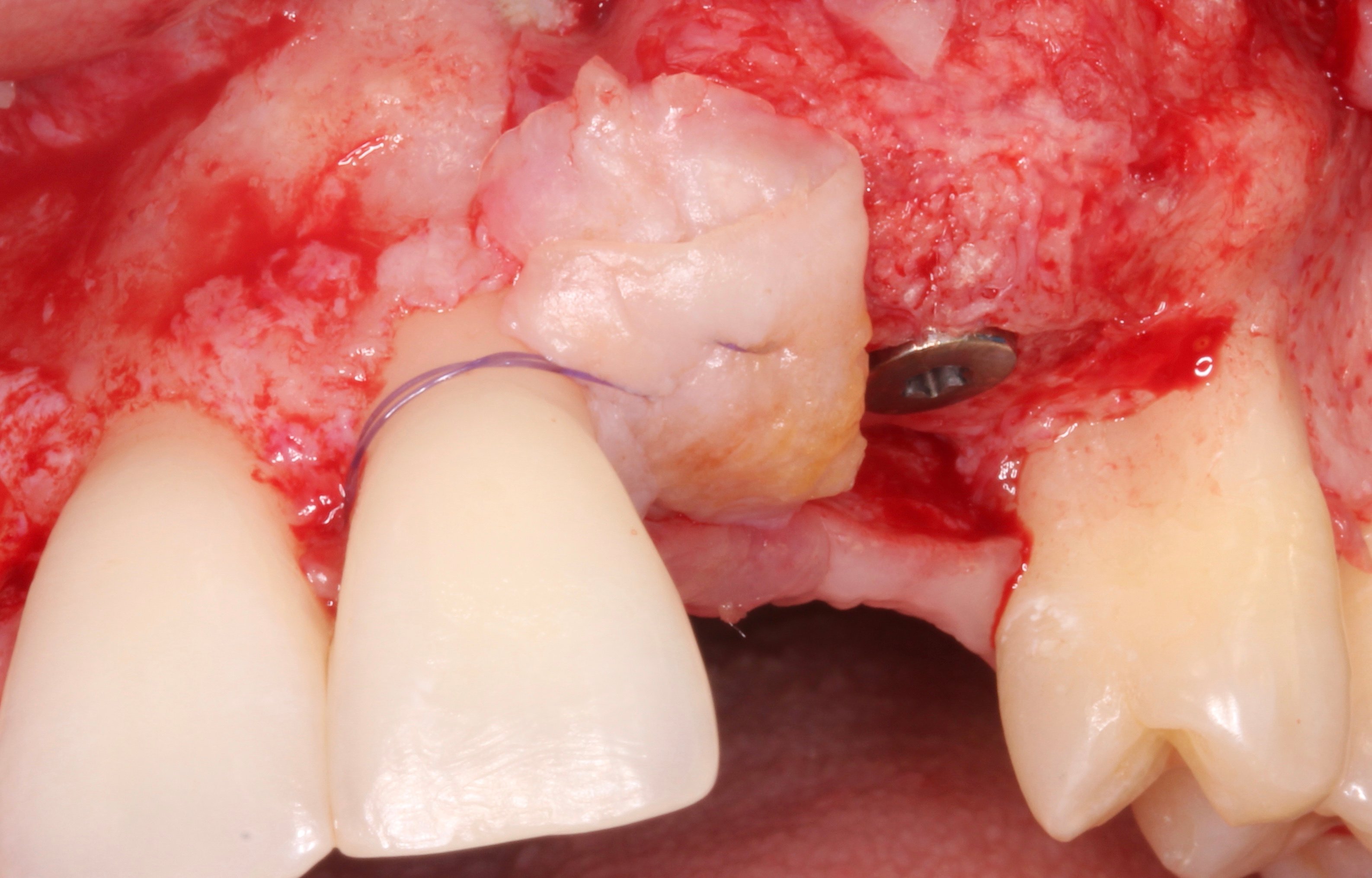
Figure 15.
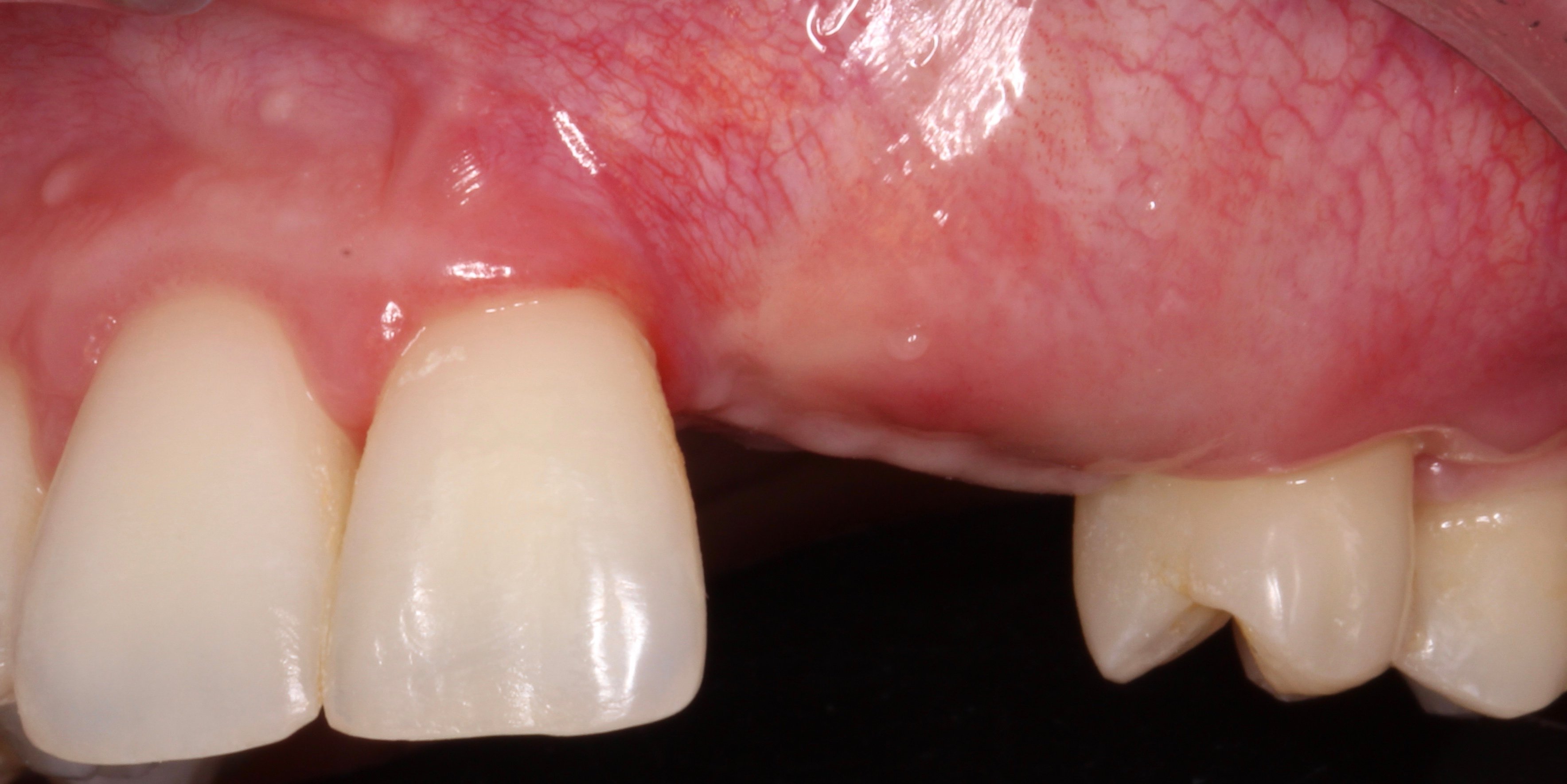
Figure 16.
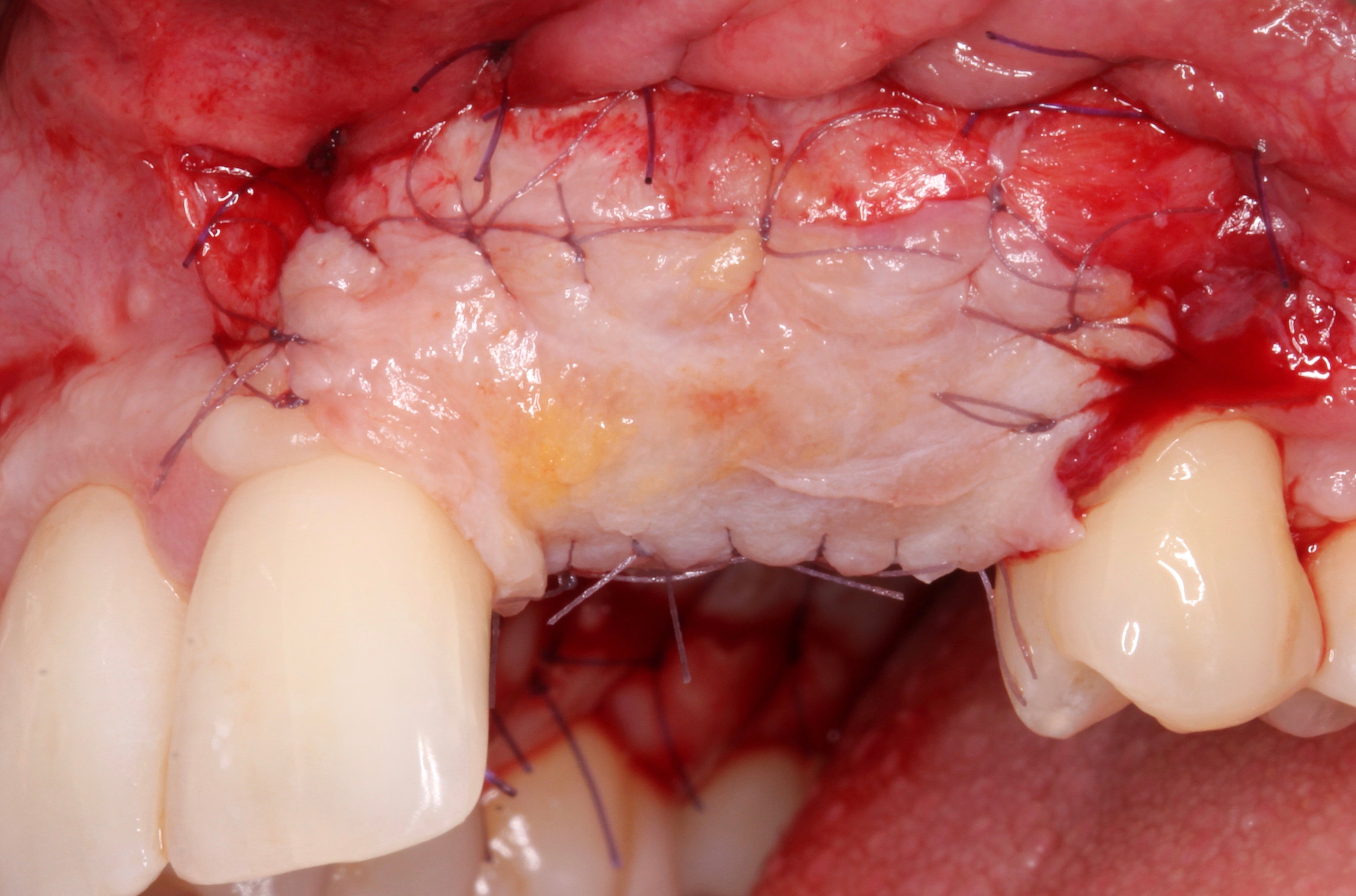
Figure 17.
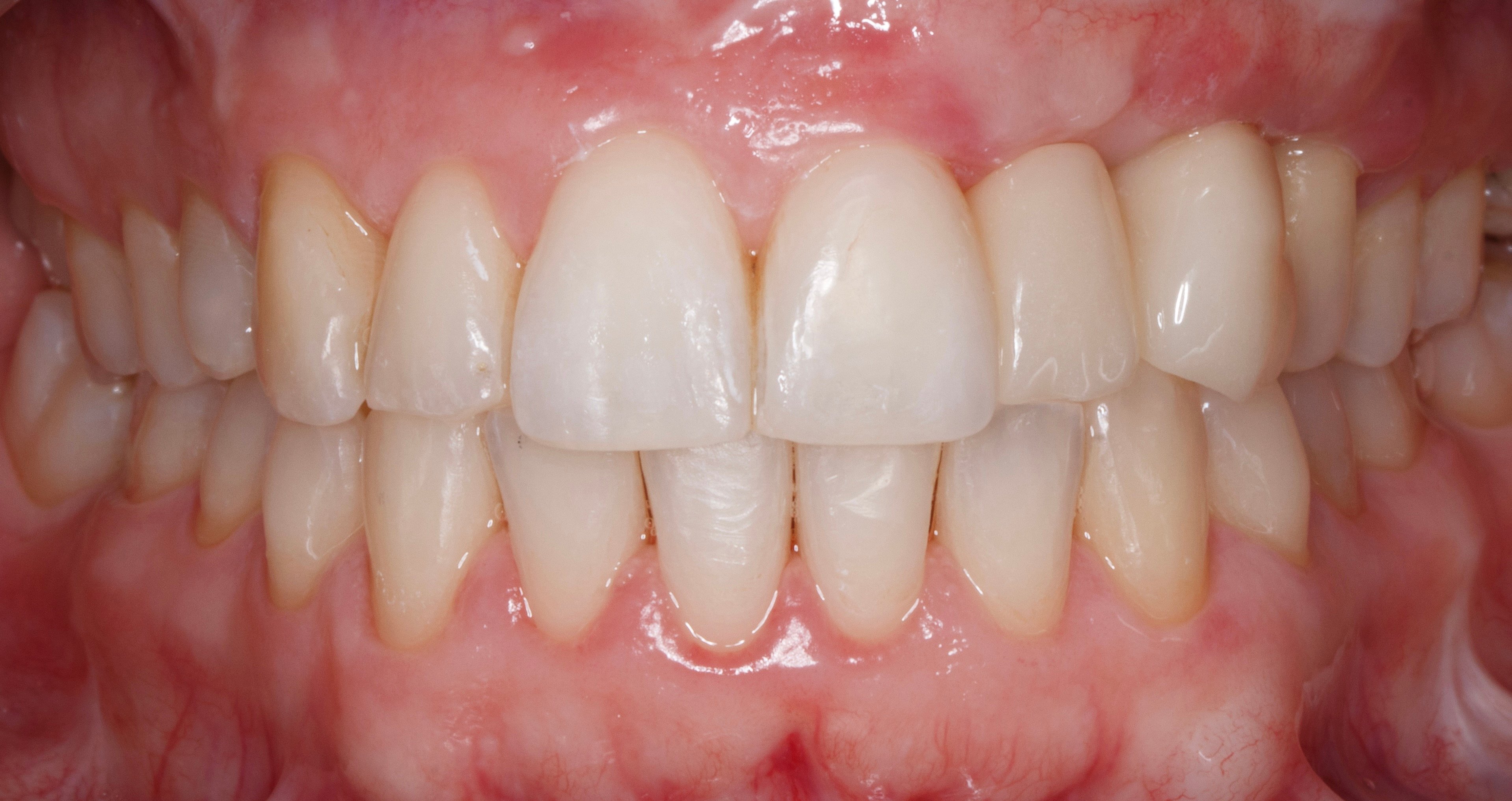
Figure 18.
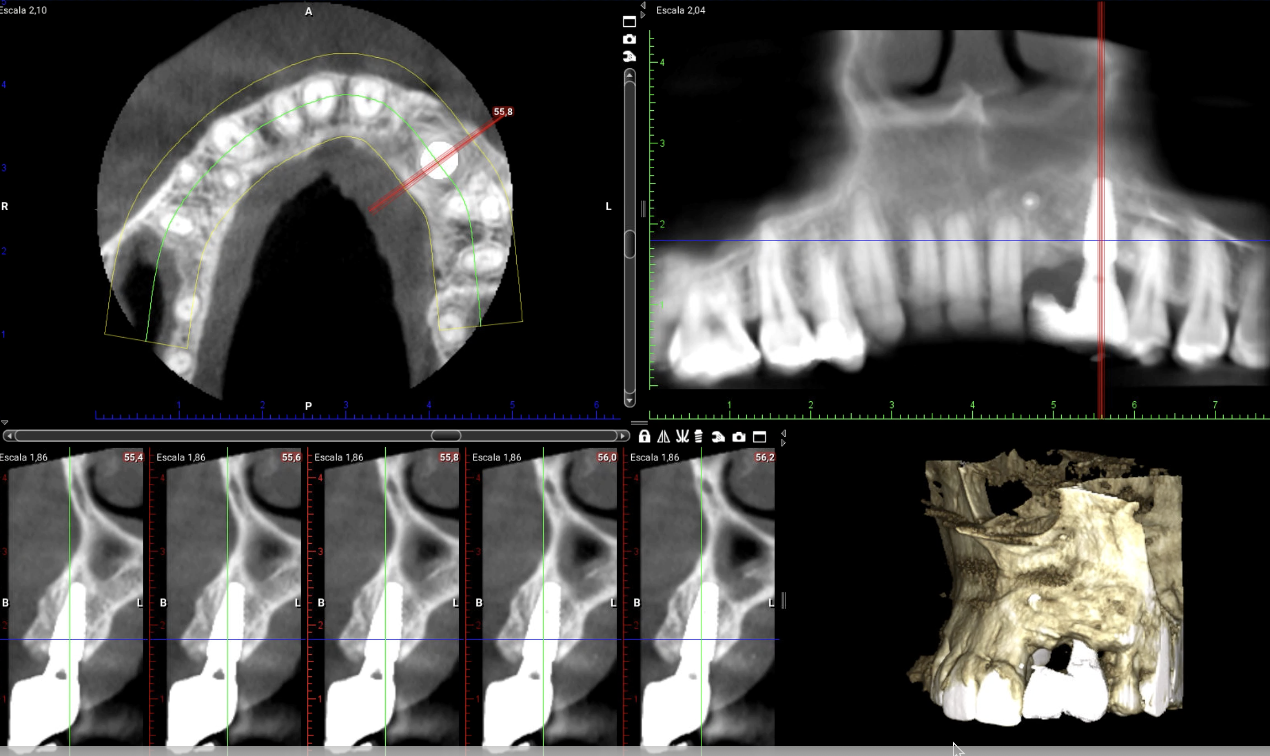
Figure 19.

